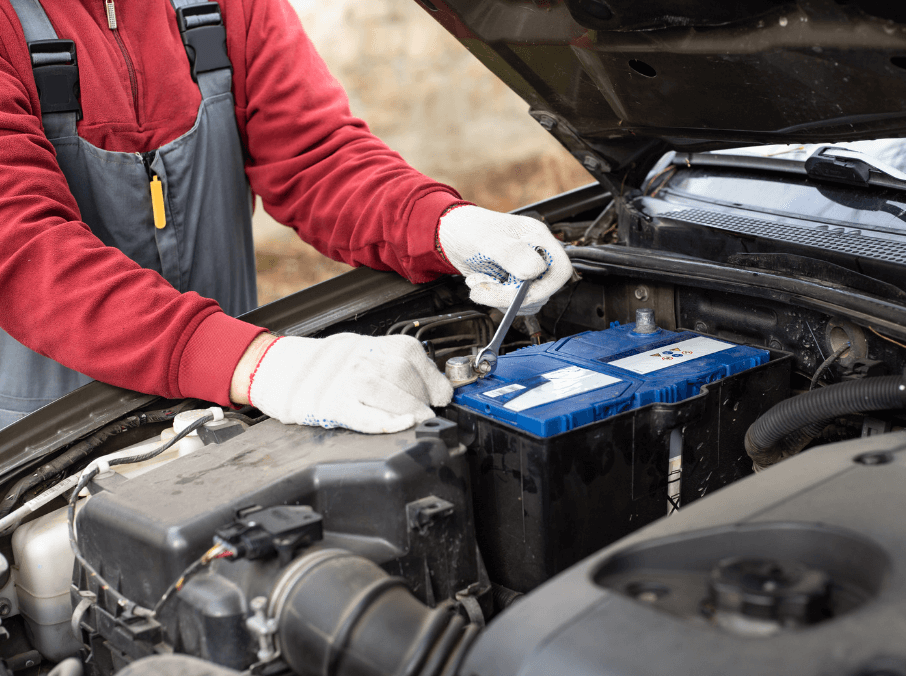
Car batteries are a fundamental component of any automobile, responsible for providing the energy needed to start the engine and run electrical components. Although most people think of car batteries as a single, uniform type of device, there are actually three main types, each with their own characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.
We will discuss these three types in detail, bring out their advantages and disadvantages to help you know more about this relationship, let’s get started.

1# Lead-acid batteries
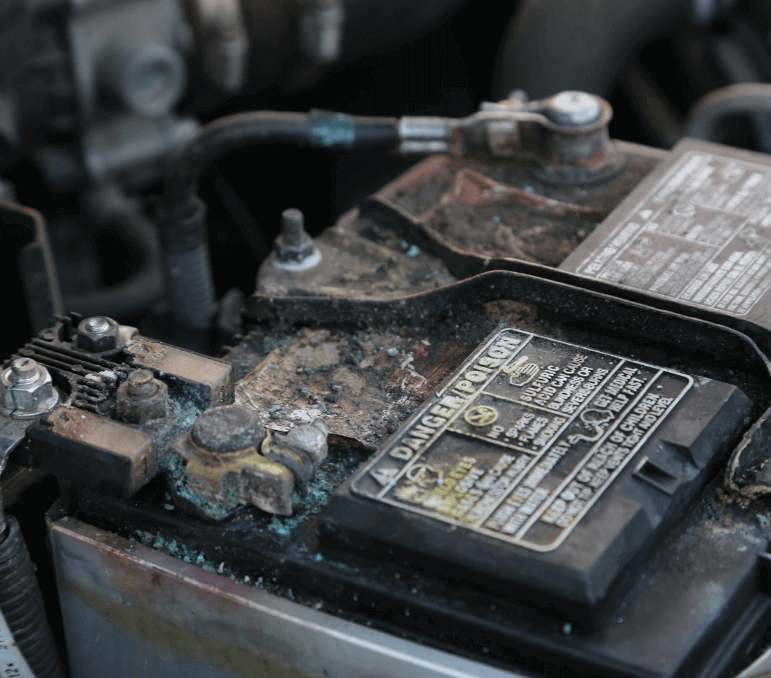
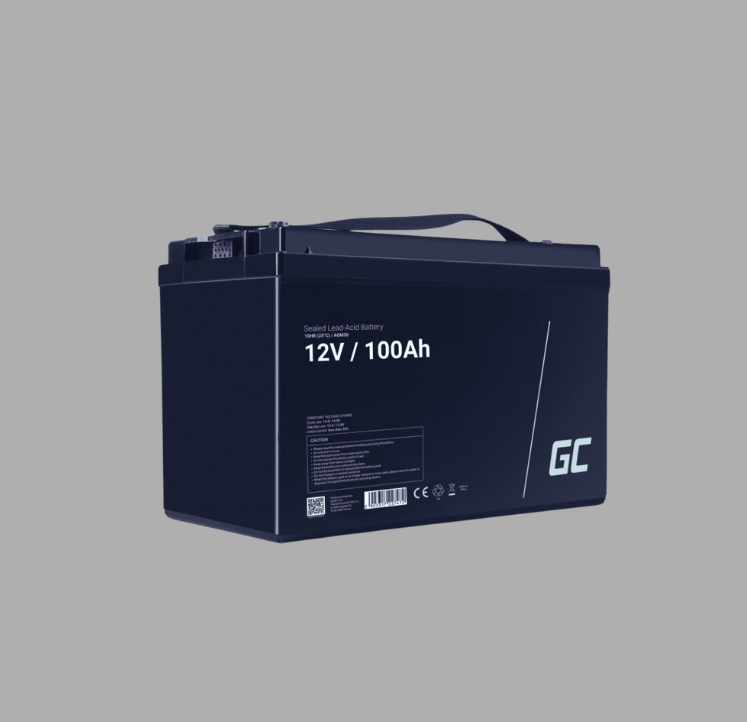
Lead-acid batteries are the most common type of car battery and have been in use for over a century. They are widely known for their cost-effectiveness and reliability. These batteries have a long history and continue to be the choice for many standard combustion-engine vehicles
Structure and function
A typical lead-acid battery is composed of lead plates and lead dioxide, which act as electrodes. These plates are immersed in a sulfuric acid electrolyte solution, which facilitates chemical reactions that generate electricity. Lead-acid batteries work based on a reversible chemical process:
Discharging Process: When the battery discharges (ie, delivers power), sulfuric acid reacts with the lead plates to form lead sulfate. In this condition, as the concentration of sulfuric acid decreases, the electrolyte weakens and the concentration of water increases.
Charging Process: During charging, this process is reversed, converting lead sulfate into lead and sulfuric acid, restoring the electrolyte to its original composition and preparing the battery for further use.
Types of lead-acid batteries
Lead-acid batteries can be classified into two subtypes: flooded lead-acid batteries and sealed lead-acid batteries (SLA).
Flooded lead-acid batteries: These are also called wet-cell batteries, where the electrolyte solution is free to circulate. They require regular maintenance, including topping off with distilled water to compensate for water loss during electrolysis.
Sealed lead-acid batteries (SLA): These are maintenance-free and designed to prevent any leakage of electrolyte. SLA has gel and absorbed glass mat (AGM) variants.
Lead-acid batteries are most commonly used:
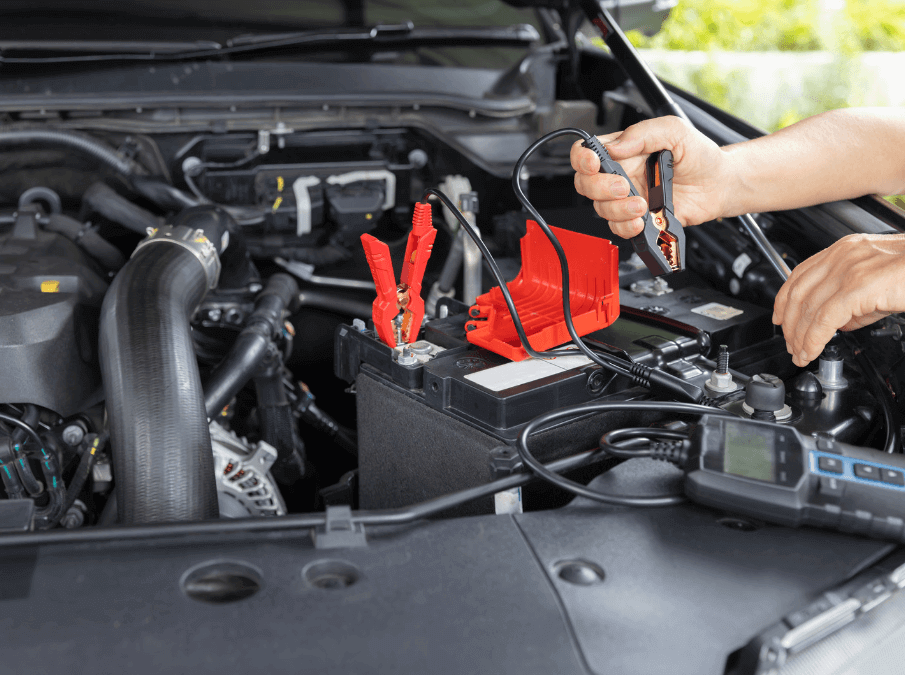
Automobiles (Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles): Lead-acid batteries are widely used in traditional gas-powered vehicles to provide the initial power to start the engine. These batteries are essential for powering the starter motor, ignition system, and other electrical components before the alternator takes over once the engine is running.
Backup Power Systems: Lead-acid batteries are commonly used in Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems for backup power in homes, offices, and data centers. They provide a reliable source of electricity during power outages.
Electric Vehicles (Older Models): While newer electric vehicles tend to use lithium-ion batteries, lead-acid batteries were used in older models and some hybrid vehicles, particularly for auxiliary functions like powering lights and entertainment systems.
Marine Applications: Many boats and marine vessels use lead-acid batteries for starting the engine and powering electrical systems such as navigation, communication, and lighting.
Off-Grid Solar Power Systems: Lead-acid batteries are frequently used in renewable energy systems, particularly in off-grid solar power setups, to store energy generated by solar panels for later use.
Motorcycles, Scooters, and Other Small Vehicles: Lead-acid batteries are commonly used in smaller vehicles like motorcycles, scooters, and ATVs to start the engine and power lights and other accessories.
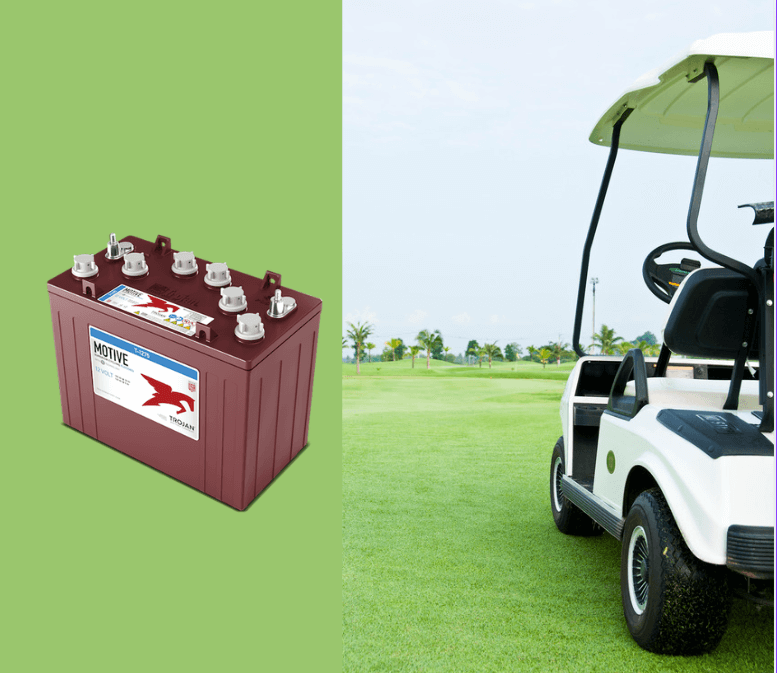
Golf Carts and Electric Utility Vehicles: Many golf carts, forklifts, and electric utility vehicles still rely on lead-acid batteries for their power supply, offering a cost-effective energy source for lower-speed vehicles.
Emergency Lighting Systems: Lead-acid batteries are often used in emergency lighting systems in commercial and residential buildings to ensure that lights remain operational during power failures.
Wheelchairs and Mobility Scooters: Lead-acid batteries are used in electric wheelchairs and mobility scooters to provide reliable power for extended periods of use.
These applications demonstrate the versatility and dependability of lead-acid batteries, making them a popular choice in various industries despite the rise of newer battery technologies.
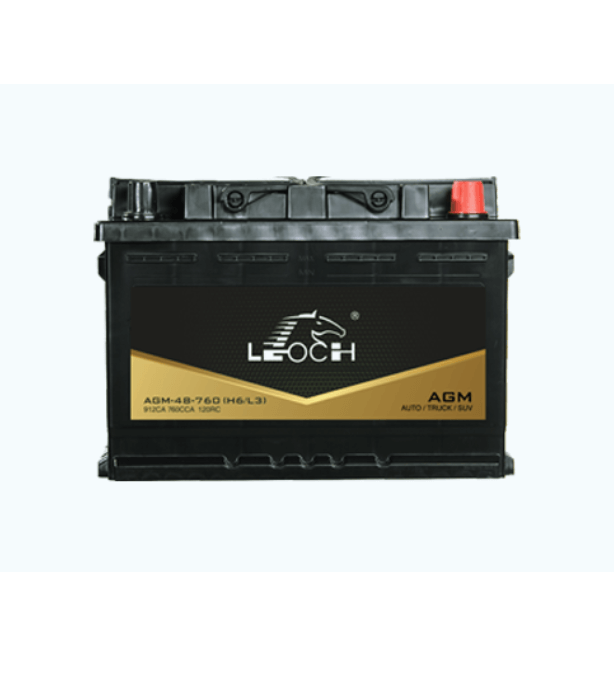
2# Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) Battery
Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) batteries are an improved version of lead-acid batteries. They are designed to provide improved performance, higher durability, and increased safety. AGM batteries are considered a more advanced type of sealed lead-acid battery and are becoming more popular in modern vehicles, especially luxury models and vehicles with start-stop systems.
Structure and function
AGM batteries use a design where the sulfuric acid electrolyte is absorbed into a fine fiberglass mat that sits between the battery’s plates. This construction offers several advantages over traditional flooded lead-acid batteries.
Vibration resistance: The fiberglass mat keeps the electrolyte in place, providing better protection against vibration and shock, which can damage conventional flooded batteries.
Sealed and maintenance-free: AGM batteries are sealed and do not require regular addition of water unlike their flooded counterparts. This makes them a true “install-and-forget” solution.
Faster charging: AGM batteries charge faster than conventional lead-acid batteries because they have lower internal resistance.