Hello friends, you know that when a car is not used regularly, the battery can degrade or lose charge, causing unnecessary costs and inconvenience when you need your car again.
Understanding how to maintain your car battery during periods of inactivity can significantly extend its lifespan and ensure your vehicle is ready to go when needed.
We’ll cover the various factors that affect car battery health and offer expert advice on maintaining your battery when not in use.
By following these tips, you can avoid premature battery failure and enjoy reliable performance even after extended periods of storage.
First you need to understand the nature of batteries
Car batteries, usually lead-acid batteries, work through a chemical reaction that produces electricity.
Over time, this chemical process becomes less efficient and a battery’s ability to hold a charge decreases. This degradation can be accelerated by environmental factors, usage patterns and battery age.

There are several types of car batteries
Lead-Acid Battery: The most common type found in vehicles with two primary variations:
Flooded Lead-Acid (FLA): Requires occasional maintenance, such as topping up with distilled water.
Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM): These are maintenance-free batteries that are more resistant to deep discharge and generally have a longer lifespan.
Lithium-ion batteries: rare in conventional vehicles but common in electric vehicles (EVs).
How long can battery life be?
Car batteries typically last between 3-5 years, although this can vary depending on climate, driving habits and maintenance. A battery that is left unused can degrade very quickly, especially if not properly maintained.
Why Maintaining Your Car Battery Is Essential When Not in Use
When a car sits idle for an extended period, several factors can cause the battery to lose its charge. These include:
Parasitic drain: Even when the car is off, certain systems (such as the clock, security system, and other electronics) continue to draw a small amount of power from the battery. Over time, this can deplete the battery’s charge.
Temperature extremes: Both hot and cold temperatures can adversely affect the battery’s chemical composition.
Heat speeds up the chemical reaction inside the battery, causing it to degrade faster, while cold temperatures can make the battery less efficient and difficult to charge.
Natural self-discharge: Batteries naturally lose charge over time, even without any external drain.
To avoid being greeted by a dead battery when you return to your car after a long period of inactivity, you must take steps to maintain it.
Disconnect your battery easily
One of the easiest ways to prevent battery drain is to disconnect the battery from the vehicle. By removing the negative terminal (black wire), you can stop any parasitic drain caused by your vehicle’s electrical system.
You need to take this step to disconnect the battery
Turn off the vehicle and remove the key from the ignition.
Open the hood and locate the battery. Locate the negative terminal, which is usually marked with a minus (-) sign.
Using a wrench, loosen the nut on the negative terminal and carefully remove the wire.
If necessary, remove the positive terminal as well. Make sure cables are secured away from battery terminals to avoid accidental contact.
Note: While this procedure prevents parasitic drain, it can also reset your vehicle’s electronic systems, such as the clock and radio settings.
Use a trickle charger or battery maintainer easily
A trickle charger or battery maintainer is one of the best ways to ensure your car battery stays fully charged when not in use.
These devices provide a low-level charge that compensates for the battery’s normal self-discharge, preventing it from flatlining.
There are several battery charger types you need to know
Trickle charger: Provides a constant low charge to the battery, ensuring that it remains fully charged.
However, trickle chargers can overcharge batteries if left unattended for too long.
Battery Maintainer: A smart version of the trickle charger, it monitors battery charge and supplies power only when needed, making it ideal for long-term storage.
How to use your battery maintainer:
Connect the charger wires to the corresponding terminals (positive to positive, negative to negative).
Plug the charger into a power outlet and let it manage the battery charge over time.
Check the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific charger and battery type to avoid overcharging or damage.
You now start your car in phases
If possible, starting your car every two weeks and allowing it to run for at least 15-20 minutes can help keep the battery charged.
When the engine runs, the alternator recharges the battery.
However, this method is less reliable than using a battery maintainer, as the battery may not fully recharge for a short period of time, especially if the car has been sitting in cold weather.
We will give you some extremely important tips
Try to drive short distances without letting the car idle. This will ensure the battery recharges properly and prevent other components such as tires and fluids from corroding.
Avoid running accessories such as air conditioners, headlights or radios, which can place a significant load on the battery and prevent it from charging effectively.
Store the car in an ideal environment. Where you store your car can have a significant impact on the longevity of your battery.
Both extreme heat and extreme cold can accelerate the deterioration of car batteries.
Best tips for savings:
Climate-controlled garage: If possible, store your vehicle in a climate-controlled environment to protect the battery from extreme temperatures.
Use a car cover: If you don’t have access to a garage, using a high-quality car cover can help reduce temperature fluctuations, especially from the sun, which can heat up the engine bay and negatively affect the battery.
Avoid concrete floors: There is a common belief that storing batteries on a concrete floor can cause them to lose charge.
Although modern battery designs are less prone to this, it’s still a good idea to store your battery on a wooden block or insulated surface to avoid potential problems.
Use a battery isolation kit If you live in an area where temperatures frequently drop below freezing, a battery insulation kit can help protect the battery from the cold.
These kits are made from heat-resistant materials and wrap around the battery to keep it at a stable temperature.
There are several benefits of using insulation kits such as:
Helps maintain optimal operating temperature for the battery.
Reduces the risk of freezing, which can cause irreparable battery damage.
In cold weather, this helps maintain battery charge, as batteries lose capacity faster in the cold.
Battery isolation kits are available at most auto parts stores and can be easily installed at home.
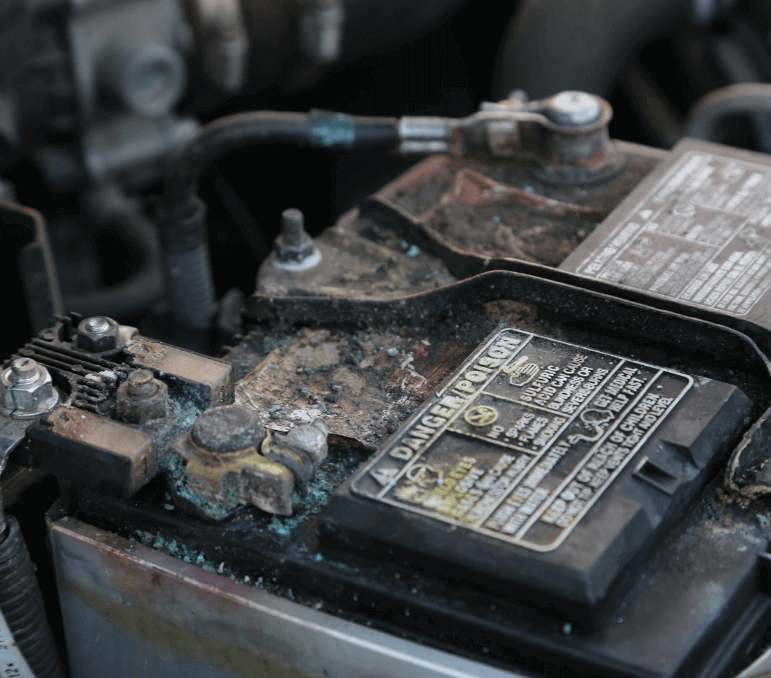
How to clean your battery terminals:
First, disconnect the battery.
Make a paste using baking soda and water and apply it to the terminals with a brush. Baking soda will neutralize the acid, breaking down the corrosion.
Use a stiff brush to scrub the terminals, removing any buildup.
Rinse with water and dry thoroughly before reconnecting the battery.
This simple maintenance task can prevent voltage drops and ensure a strong connection between the battery and the vehicle’s electrical system.
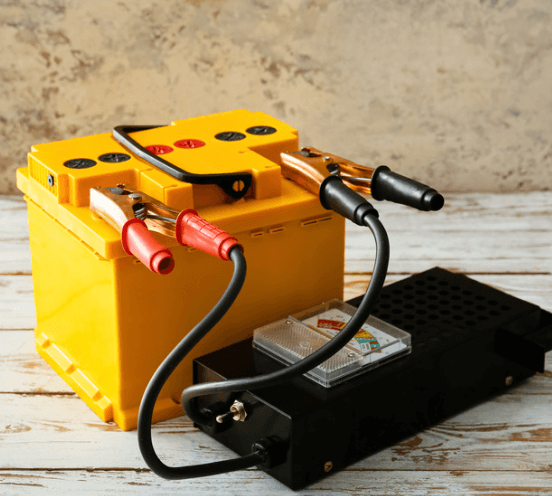
You need to use a battery tester
If you plan to keep your car idle for long periods of time, it’s a good idea to check battery health regularly using a battery tester or voltmeter.
These tools measure the voltage of the battery and can indicate whether it needs to be charged or replaced.
Few important steps to check battery voltage:
Turn off the vehicle and remove the key from the ignition.
Connect the voltmeter to the corresponding battery terminal.
A healthy car battery should have a voltage reading between 12.4 and 12.7 volts.
If the reading is below 12.4 volts, the battery may need to be charged.
Periodically checking your battery allows you to catch any problems before they become serious, preventing unexpected failures when your vehicle needs them.
You should avoid deep discharge
Lead-acid batteries are not designed to be completely discharged. A deep discharge occurs when the battery is drained below 20% of its capacity, which can significantly reduce its life. Even some deep discharges can cause permanent damage to battery cells.
Some of the best ways to avoid deep discharge are:
Use a battery maintainer or trickle charger to keep the battery charged.
If the battery has been unused for a long time, make sure it is fully charged before attempting to start the vehicle.
Avoid operating items such as lights or the radio while the engine is off, as this can quickly drain the battery.
Replace the battery if necessary
No matter how well you maintain your car battery, it will eventually reach its lifespan. If you notice that the battery is struggling to hold a charge, or if it is older than 4-5 years, it may be time to replace it.
Some signs that your battery needs to be replaced:
- The battery takes longer than usual to start the car.
- Frequent need for jump-starts.
- Swelling or swelling of the battery case.
- Visible corrosion on terminals that cannot be cleaned.
- When replacing the battery, be sure to choose a high-quality replacement that meets your vehicle’s specifications.
Regular maintenance and proactive care will not only save you time and money but also contribute to the overall longevity and performance of your vehicle.
Whether you’re storing your car for a few weeks or several months, these expert tips will help keep your battery in optimal condition, ensuring a smooth start every time.