Over the years, I’ve found that a common question car owners ask is, “What voltage is too low for a car battery?”
We’ve all seen it – sitting in the driver seat, turning the key, only to hear that dreaded click. It’s a moment that can make you wonder, what voltage is too low for your car battery.
I’ll walk you through everything you need to know about car battery voltage, and what you can do when something starts to go wrong.
By the end of this, you’ll have a clear understanding of how voltage works and how to prevent problems before they happen.
What Voltage is Too Low for a Car Battery?
To start with, let’s look at the basic voltage levels of a car battery. A healthy, fully charged car battery should read around 12.6 volts when the engine is off.
This is considered the optimal voltage for a standard lead-acid battery. If the voltage dips below 12.4 volts, your battery is starting to lose charge.
When it falls to 12.0 volts or lower, it’s time to pay attention.
When your battery reads below 11.8 volts, it’s most likely too low to start your car. At this point, the car electrical system struggles to function properly.
The battery simply doesn’t have enough power to handle even basic functions like starting the engine or powering the lights.
In simple terms, a car battery with a voltage this low is close to failure and likely needs charging or replacement.
How Does Car Battery Voltage Work?
The voltage in a car battery reflects the energy stored within the battery. A healthy battery stores electrical energy that can be drawn on by the vehicle systems when needed.
If you imagine your car electrical system as a network of roads, the voltage acts as the fuel that powers the vehicles—your lights, engine, radio, and other electrical components.
When you turn the ignition key, the car starter motor demands a large surge of power to get the engine turning.
This draws energy from the battery. If your battery’s voltage is too low, it won’t be able to supply enough energy to get the engine cranked.
How to Measure Your Car Battery Voltage
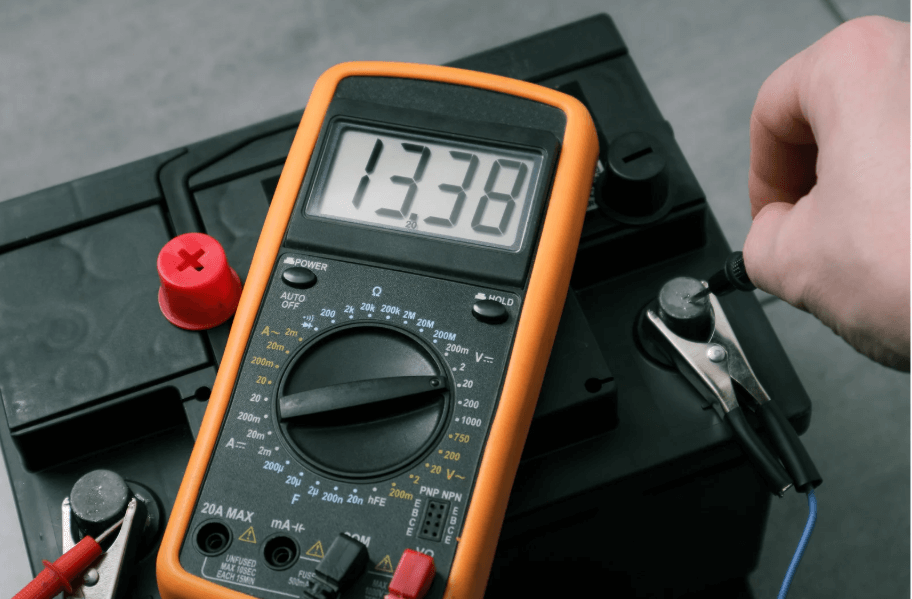
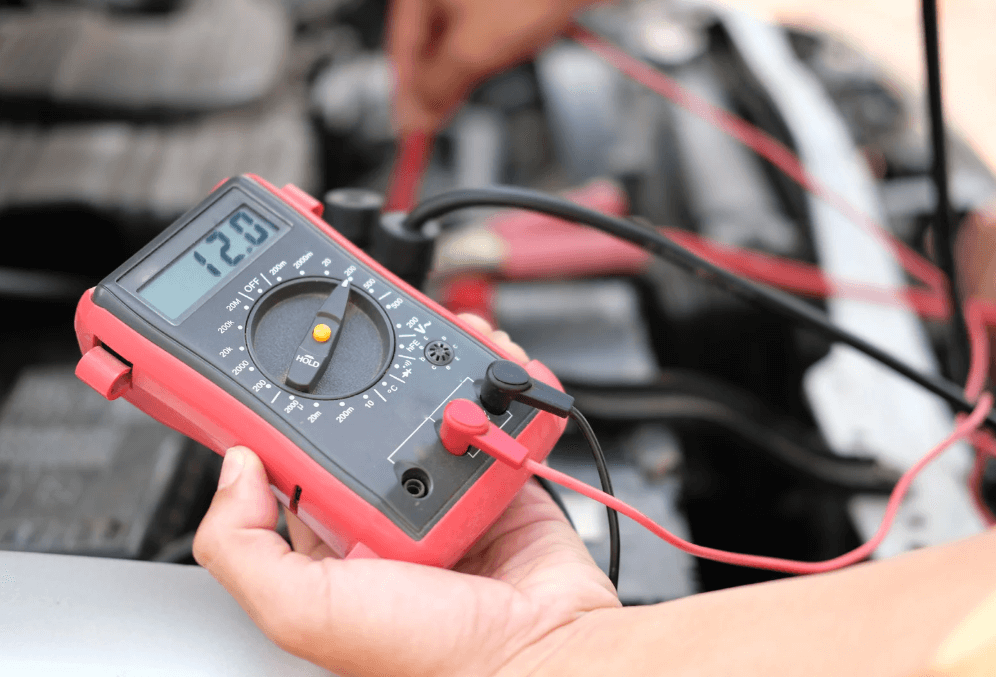
Before jumping to conclusions, it’s a good idea to measure the voltage of your car’s battery.
Doing this is easy and doesn’t require advanced knowledge. All you need is a digital multimeter, which is a tool that measures electrical properties.
Here’s how to measure the battery voltage:
Turn off the car: Make sure your car is not running, as this can affect the voltage reading.
Set the multimeter to DC volts: DC (Direct Current) is the type of voltage a car battery uses.
Connect the multimeter leads: Attach the red lead to the positive terminal of the battery and the black lead to the negative terminal.
Check the reading: A healthy, fully charged battery should show around 12.6 volts. Anything lower than 12.4 volts indicates that the battery is undercharged, and a reading below 11.8 volts means the battery is too low to start the car.
If your multimeter reads below 12.0 volts, you should consider charging the battery or investigating further for potential issues with the alternator or other electrical components.
Why Does Car Battery Voltage Drop?
Several factors contribute to a drop in battery voltage. Here’s a closer look at some of the common reasons:
1. Battery Age
Like all things, a battery’s performance tends to degrade over time. Most car batteries last about 3 to 5 years depending on how often they are used and how well they are maintained.
As the battery ages, its capacity to hold a charge decreases, leading to lower voltage readings.
2. Faulty Alternator
The alternator is responsible for recharging the battery while the engine is running.
If your alternator is malfunctioning, it might not properly charge the battery, leading to a gradual decrease in voltage.
If you notice your battery keeps draining even after charging, the alternator could be the culprit.
3. Electrical Drains
Sometimes, the battery’s voltage can be drained by electrical components in your car that continue to draw power, even when the car is off. This can be caused by issues like:
A glowing dashboard light or alarm system that stays on
A faulty switch that keeps certain electrical systems running
If the battery’s voltage is draining too quickly, you might not notice it until you try to start the car, and by then, it could be too late.
4. Extreme Weather Conditions
Cold temperatures can have a significant effect on your car battery’s voltage.
In cold weather, the chemical reactions inside the battery slow down, which reduces the battery’s capacity.
This means your battery will lose charge more quickly and might struggle to provide enough power to start the car.
In extremely hot conditions, your battery is at risk of losing water, which can lead to lower voltage and eventual damage.
Symptoms of Low Battery Voltage
If your car battery voltage is low, you might start noticing several symptoms:
Difficulty Starting the Car: If you notice that the engine cranks more slowly than usual or doesn’t start on the first attempt, your battery could be the problem.
Dim or Flickering Lights: When you turn on your car’s headlights or interior lights, a low voltage battery can cause them to appear dim or flicker.
Electrical System Failures: Many electrical systems in your car rely on the battery. If the voltage is low, you might experience issues with power windows, air conditioning, or even the radio.
Battery Warning Light: Most modern cars have a dashboard light that illuminates when the battery is having trouble. This could mean low voltage or an issue with the charging system.
Clicking Sound: When you turn the ignition key, a clicking sound is often a sign that the battery doesn’t have enough charge to turn the engine over.
What to Do When the Voltage Is Too Low?
So, you’ve measured your car battery voltage and found it’ too low. What now?
1. Recharge the Battery
If the battery voltage is below 12.0 volts but above 11.8 volts, try recharging it. You can do this by connecting your car to a battery charger and allowing it to charge. This can take several hours depending on how low the voltage is.
2. Jumpstart the Car
If your car won’t start, jumpstarting the battery using jumper cables and another vehicle can provide the boost you need. Make sure you connect the positive and negative leads correctly, or you could risk damaging the electrical system.
3. Check the Alternator
If your battery keeps losing charge, even after recharging or jumpstarting, the alternator could be at fault. Have it tested at an auto parts store or by a mechanic. If it’s defective, you’ll need to replace it to prevent further issues.
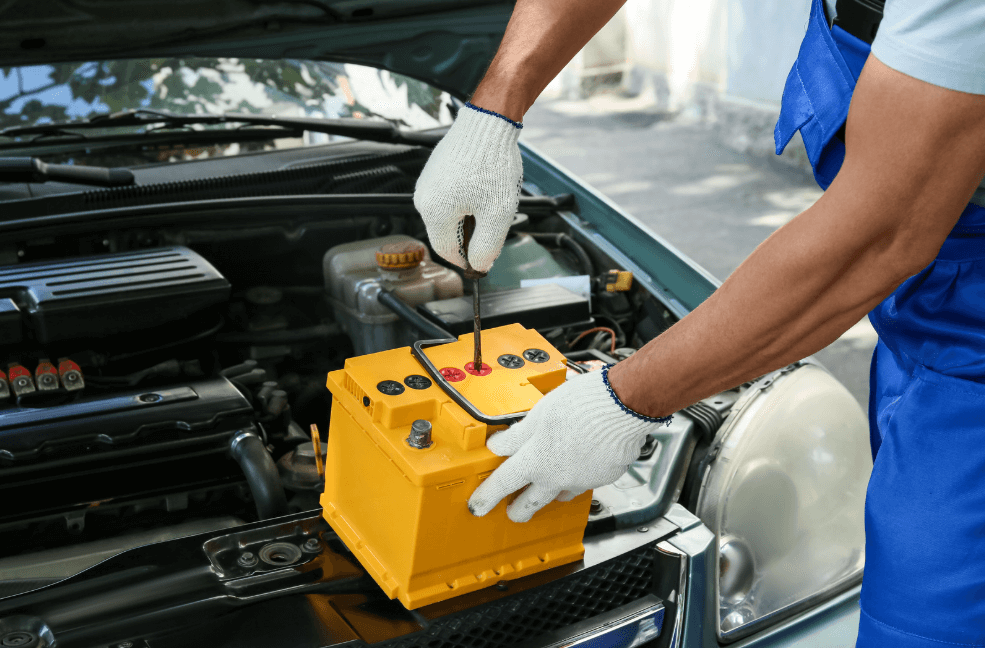
4. Replace the Battery
If your battery is old (more than 3 years) or has sustained significant damage, it may be time to replace it. A professional can help you find the right battery for your car model and ensure proper installation.
Conclusion
To wrap things up, keeping an eye on your car battery’s voltage is an important part of vehicle maintenance.
A healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts when the engine is off. Anything below 12.0 volts may indicate that your battery is undercharged, and anything below 11.8 volts is typically too low to start the engine.
By checking your battery’s voltage regularly, paying attention to warning signs, and maintaining your car electrical systems, you can ensure that your car runs smoothly without unexpected battery failures.