If you’ve ever wondered about your car battery and the voltage it should have when your vehicle is off, you’re not alone.
It’s one of those things most drivers don’t think about until something goes wrong. But trust me, knowing the normal battery voltage when the car is off can save you a lot of stress and possibly a dead car battery.
I’ll walk you through everything you need to know about your car battery voltage.
From the ideal voltage when your car is off to how to check it, I’ll cover all the details in a simple, easy-to-understand way.
What Is Normal Battery Voltage When the Car Is Off?
When your car is off, your car battery should ideally show a voltage of around 12.6 volts. This is considered the standard voltage for a healthy, fully charged car battery. But why exactly is this number so important?
A fully charged battery at rest (engine off) measures about 12.6 volts because that’s the power the battery holds after being charged by the alternator.
If your battery is lower than this, like at 12.4 volts, it means your battery is losing its charge, and if it drops to 12.0 volts or below, it could be a sign that the battery is getting weak and may need to be replaced soon.
How to Check Your Car Battery Voltage
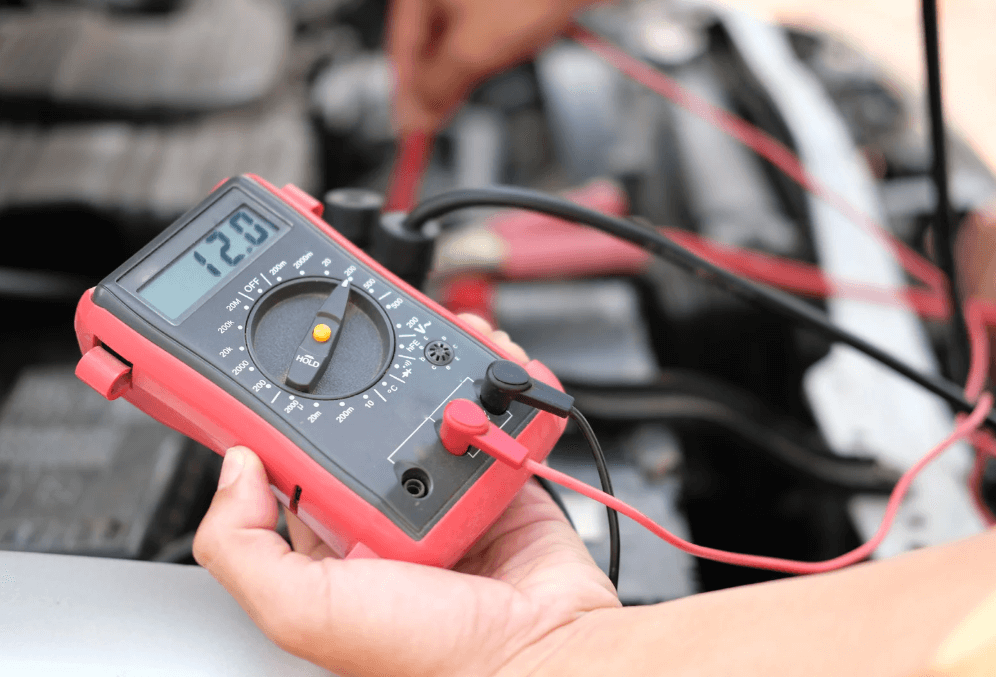
Checking your car’s battery voltage is a simple task, even if you’re not familiar with car maintenance.
The first thing you’ll need is a digital multimeter, which is an easy-to-use tool that measures electrical voltage. You can pick one up at a hardware store or online.
Start by turning off your car. It’s essential to check the battery while the vehicle is off to get an accurate reading.
Once the car is off, set the multimeter to measure DC voltage, since your car battery uses direct current (DC) rather than alternating current (AC).
Next, take the multimeter’s red (positive) probe and connect it to the positive terminal of the battery.
The positive terminal is usually marked with a plus sign (+) or the letter “P.” Then, take the black (negative) probe and attach it to the negative terminal, marked with a minus sign (-) or “N.”
With the multimeter probes in place, look at the reading on the screen.
A healthy, fully charged battery should show around 12.6 volts.
If your reading is lower, like 12.4 volts, it means your battery is still charged but not at full capacity.
Anything lower than 12.0 volts could suggest that the battery is losing charge and may need attention.
Checking your battery’s voltage is a simple and effective way to assess its health.
If you’re unsure about the results, or if the voltage is lower than expected, it’s always a good idea to have the battery tested by a professional or take your car to an auto parts store for a more thorough check.
What Is Normal Battery Voltage While Driving?
While you’re driving, the battery’s voltage should be higher than when the car is off.
When your car is running, the alternator is charging the battery, which raises the voltage to somewhere between 13.7 and 14.7 volts.
If the voltage while driving is lower than this range, it could indicate a problem with your alternator or the battery itself.
A voltage that’s too high could mean the alternator is overcharging the battery, which could lead to damage. Ideally, your car electrical system should be able to maintain this range during your drive.
How Many Volts Is a Car Battery When Fully Charged?
A fully charged car battery should measure about 12.6 volts when the car is off. This is the standard voltage of a healthy battery at rest.
When fully charged, the battery has enough power to run your car electrical systems, start the engine, and handle other electrical demands.
If your battery measures 12.4 volts, it’s still in decent condition but has lost a little charge. Anything lower, like 12.0 volts, could signal that your battery is losing its charge and may need attention soon.
What Happens If Your Car Battery Voltage Is Too Low?
If your car battery voltage is too low, it can cause a variety of issues, some of which might prevent your car from starting or functioning properly.
When the voltage drops below 12.4 volts, your battery is no longer fully charged, and if it falls to 12.0 volts or below, the battery could be in trouble.
Let me break down what might happen if you don’t address low battery voltage.
First, the most noticeable effect of a low battery is difficulty starting your car.
If the voltage drops significantly, you may notice that the engine cranks slowly when you turn the key or push the start button.
This is because the battery doesn’t have enough power to turn the starter motor fast enough to start the engine. If the voltage falls too low, the car might not start at all.
In addition to hard starting, you may experience electrical problems in your car.
Low voltage can cause the headlights to appear dimmer than usual or cause flickering lights on your dashboard.
The battery is responsible for powering many of your car electrical systems, so when it’s weak, it affects everything from the lights to the air conditioning.
Another problem that low voltage can cause is erratic behavior of your car electrical components.
For instance, you might find that your radio, power windows, or other features don’t work properly.
These systems rely on a steady voltage to operate smoothly. When the battery is weak, these components can behave unpredictably or stop working altogether.
Lastly, a consistently low voltage can also put extra strain on your car alternator.
The alternator is responsible for charging the battery while the engine is running.
If the battery isn’t holding enough charge, the alternator has to work overtime, which could lead to alternator failure over time. Replacing a failing alternator can be expensive, so it’s important to catch battery issues early.
How to Maintain Your Car Battery Voltage

1. Regularly Check the Battery Voltage
The first step in maintaining your battery voltage is to regularly check its status. Use a multimeter to measure the voltage when the car is off.
A healthy, fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts. If it’s lower than this, it could be time to consider recharging the battery or checking for potential issues, such as a faulty alternator.
2. Drive Your Car Regularly
Frequent short trips don’t give your alternator enough time to recharge the battery.
Ideally, you should drive your car for at least 20 to 30 minutes at a time to ensure the alternator has enough time to recharge the battery fully.
If you don’t drive often, consider taking your car for a longer drive once a week to keep the battery charged.
3. Clean the Battery Terminals
Corrosion on the battery terminals can cause poor contact, which results in low voltage and charging issues.
Regularly check the battery terminals for corrosion, which often appears as a white, chalky substance around the connections.
To clean the terminals, use a mixture of baking soda and water to gently scrub the area. Afterward, dry the terminals with a clean cloth and reattach the cables securely.
4. Ensure the Battery is Properly Secured
A loose battery can cause problems with the electrical connection, leading to low voltage or poor charging.
Make sure the battery is tightly secured in its tray and that the terminals are properly connected.
If the battery isn’t securely mounted, it could also experience vibrations that might cause internal damage, further affecting its performance.
5. Keep the Battery Charged
If your battery isn’t holding a charge, it might be due to a weak alternator, a parasitic drain, or simply an aging battery.
Keeping your battery charged is crucial for its longevity.
If you’re having trouble starting your car or the voltage is low, consider using a battery charger to top up the charge or visit an auto parts store to get your battery tested.
6. Check for Parasitic Drains
Parasitic drains happen when an electrical component in your car continues to draw power from the battery even when the car is turned off.
Common culprits include faulty lights, malfunctioning sensors, or a car alarm that isn’t working correctly.
If you notice your battery voltage dropping even when your car is not in use, it’s worth getting the electrical system checked for parasitic drains.
7. Avoid Extreme Temperatures
Extreme heat and cold can be harmful to your car battery and cause the voltage to drop.
If possible, try to park your car in a shaded or garage area to avoid excessive heat. During winter, you might want to use a battery blanket to help keep the battery at an optimal temperature.
Keeping your car in a more moderate environment will help the battery last longer and maintain a proper voltage.
8. Replace the Battery When Necessary
Even with the best care, all car batteries eventually wear out. On average, a battery lasts about 3 to 5 years, but it can vary depending on your driving habits and climate.
If you notice that your car is struggling to start, the electrical systems are acting up, or your battery voltage is consistently low, it might be time to replace the battery.
Replacing the battery before it completely dies will prevent unexpected failures.
9. Ensure Proper Alternator Function
The alternator is responsible for keeping your battery charged while your car is running. If the alternator isn’t working properly, it can cause your battery to lose charge.
Have your alternator checked regularly to ensure it’s functioning properly, especially if you notice dimming headlights, dashboard warning lights, or a weak battery.
What Can Cause Low Battery Voltage?
Several factors can cause your car battery voltage to drop, and understanding them can help you prevent potential issues before they get worse. most common causes of low battery voltage in cars.
1. Battery Age
As a car battery gets older, its ability to hold a charge naturally decreases. Most car batteries last between 3 to 5 years, but as they age, their internal chemical reactions become less efficient.
This means that the battery voltage will gradually drop over time, and eventually, it will struggle to keep your car running smoothly.
If your battery is nearing the end of its lifespan, low voltage is often one of the first signs.
2. Extreme Weather Conditions
Both extremely hot and cold weather can affect your car battery. Cold temperatures reduce the battery ability to produce the charge needed to start your car, while hot weather can cause the battery fluid to evaporate, which leads to a loss of capacity.
In winter, you might notice your battery struggles to start the engine, and in summer, high heat might cause damage to the internal components of the battery, reducing its life.
3. Faulty Alternator
The alternator is responsible for recharging your car battery while the engine is running.
If your alternator isn’t functioning properly, it won’t be able to charge the battery effectively, leading to low voltage.
Symptoms of a faulty alternator can include dimming headlights or electrical components that stop working correctly while the car is running.
If the alternator isn’t providing enough power to charge the battery, the voltage will drop.
4. Loose or Corroded Battery Terminals
The battery terminals, where the battery cables connect to the battery, can sometimes become loose or corroded.
When this happens, the electrical connection is weakened, and the battery isn’t able to charge properly.
Corrosion can build up around the terminals, causing poor contact and making it harder for your battery to receive the charge it needs from the alternator.
Regularly checking and cleaning your battery terminals can help avoid this issue.
5. Parasitic Drain
Sometimes, something in your car might be draining power from the battery even when the car is off.
This is called parasitic drain, and it can be caused by faulty electrical components, like lights or sensors that stay on when they shouldn’t.
For example, a stuck interior light or malfunctioning electronic system can slowly drain the battery overnight. Over time, this constant drain can lead to a significant drop in voltage.
6. Short Trips
Taking a lot of short trips can prevent your alternator from fully charging the battery.
Each time you start the engine, the alternator needs time to recharge the battery, but short trips might not give it enough time to do so.
This can cause your battery to gradually lose charge over time. It’s ideal to drive for longer periods whenever possible to ensure the battery stays fully charged.
7. Undercharging or Overcharging
Both undercharging and overcharging the battery can lead to low voltage issues. If your car alternator isn’t working properly, it might not be charging the battery enough (undercharging), leading to low voltage.
On the flip side, if the alternator is overcharging the battery, it can cause excessive heat, damaging the battery and its ability to maintain a proper charge.
If either of these issues occurs, it could result in a battery that doesn’t hold its charge well.
8. Electrical System Failures
Problems with your car electrical system can also cause low battery voltage.
For instance, a malfunction in the charging system, fuses, or other components might prevent the battery from being properly charged.
Electrical issues often show up as strange behavior in your car’s electrical components, like flickering lights or intermittent power loss.
Conclusion
To sum up, knowing the normal battery voltage when the car is off is an essential part of car maintenance.
A healthy car battery at rest should show around 12.6 volts. By checking your battery voltage regularly, you can catch problems before they cause bigger issues.
If your battery voltage is too low or if you notice signs of trouble like dimming lights or slow engine cranking, it might be time to replace the battery or get it tested.